HONEY AUTHENTICITY TESTING
Beekeeping is practiced in all EU countries and is characterized by a variety of production conditions, yields and beekeeping practices. The EU members with the largest honey production (Romania, Spain, Hungary, Germany, Italy, Greece, France and Poland) are located mainly in the southern part of the European Union, where climatic conditions are more favorable for beekeeping. Despite being the second largest producer of honey in the world, the EU is a net importer of honey, as domestic production covers only about 60% of consumption. The main supplier of honey imported into the EU is China, followed by Ukraine and Latin America.
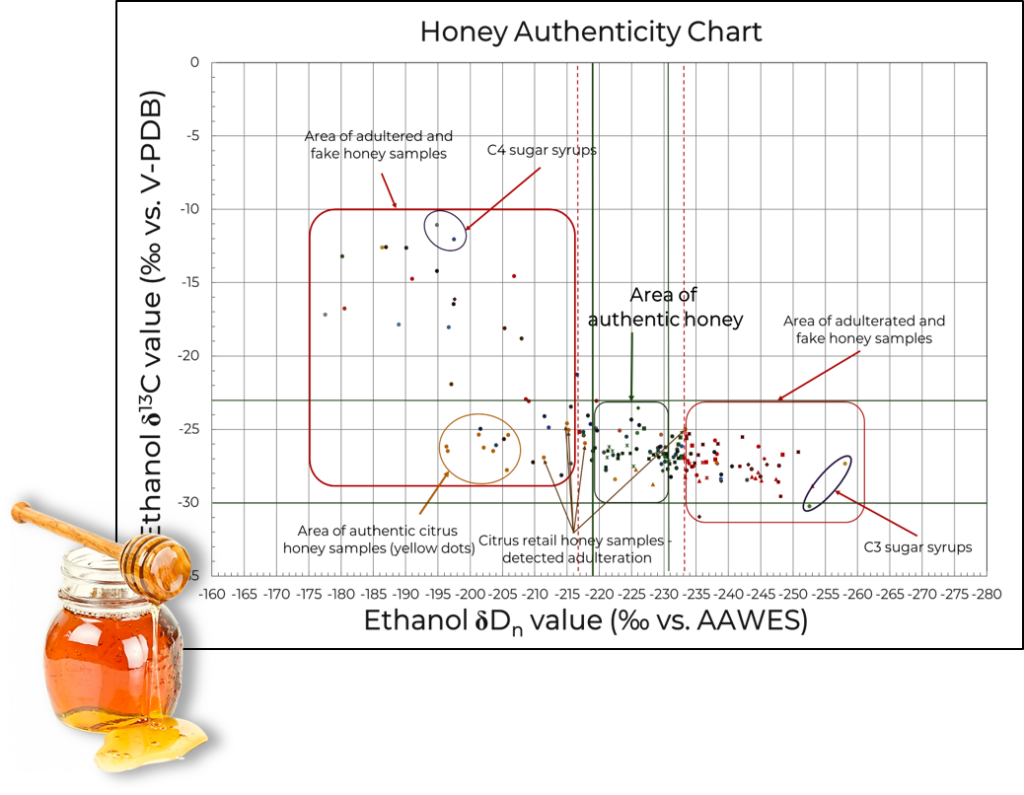
According to the European Commission, honey is on the list of TOP 10 products that are most exposed to the risk of food fraud. The Codex Alimentarius Commission has set a standard for honey to protect consumer health and ensure fair trade practices. The most common procedures are the addition of sugar and incorrectly marked geographical origin.
The scam with honey has different forms – multi-flower versus one source, diluting with sugar and adding syrup.

Direct and indirect counterfeiting of honey
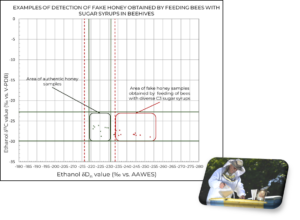
Direct adulteration of honey means mixing honey directly with industrial sugar syrup. Indirect falsification of honey means feeding bees with industrial sugar syrup. In the case of indirect dilution, bees turn industrial sugar syrup into “honey”. This type of honey counterfeit is harder to detect. This is achieved by adding sugar syrups to increase the volume or grazing ahead of time, and then by artificial drying in large “honey factories”, in order to reduce time and costs. In all cases, the final product is far inferior to what consumers think they are buying, as well as the legal definition of honey in the EU.
Adding syrup to honey
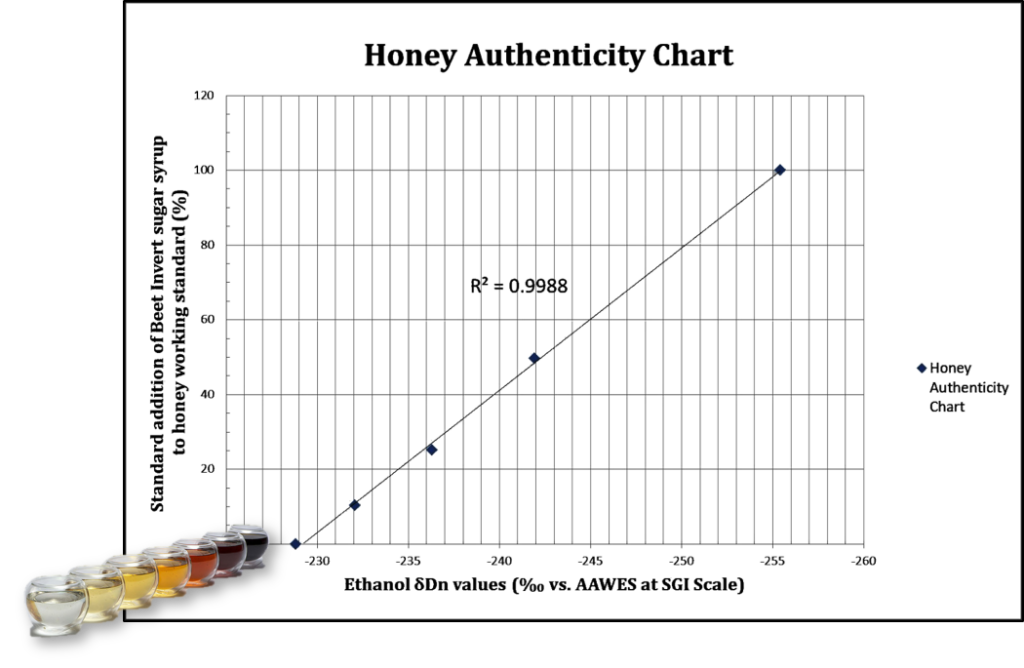
Recently, a new way of counterfeiting has appeared – using invert sugar syrup originating from sugar beet, which belongs to the C3 type of plants. By doing this, they have succeeded in overcoming known isotopic methods that are unable to detect sugars derived from C3 plants. Here, the EIM-IRMS® method differs because we are able to detect all of the above practices.
Honey testing solution:
⦾ Detection of additional C3-sugar syrup
⦾ Detection of additional C4-sugar syrup
⦾ Detection of the origin of added sugar from C3 plants